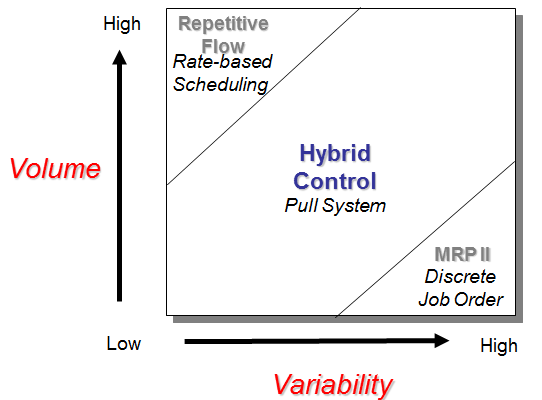
Determining an appropriate production model starts with Demand Profile and Demand Segmentation. High volume low variability items, and low volume high variability items behave very differently. How to decide if a particular product is a candidate for a one piece flow cell or a craftsmen job bench? Look to the coefficient of variation for a clue.
Type 1 – Rate-base or Just-in-time
- forecasting of the flow rate or takt time
- RCCP – rough cut capacity planning to monitor impact of mix and volume on pace maker operation
- produce to rate (or TAKT) vs discrete order or customer pull
- demand flow vs time-phased requirements planning
- maintain flow priority and timing
- no detailed Capacity Requirements Planning required
- no or minimal shop order launch or inventory transactions
- highly visual and standardized shop floor control
- “one-piece” flow, zero inventory, standard WIP – work-in-process
- seamless flow/pull of material
- Dynamic cycle time (Little’s Law)
Type 2 – Pull
- combination of discrete forecasting and/or demand rate-based forecasting
- MRP planning — pull Kanban, Heijunka visual shop floor control
- RCCP, but no detailed CRP
- flat Bills Of Materials
- more cellular manufacturing
- point-of-use vs. central stores
- inventory is strategic: standard inventory, time-based replenishment, pull based on consumption vs. push based on demand
- based on statistically balanced rate, build to level-loaded demand with calculated standard inventory buffers
Type 3 – Push or Job Shop Discrete
- discrete requirements planning (firm orders and long range forecast)
- Rough Cut Capacity Plan
- time phasing of requirements
- application of order policies: lead time, safety stock & time
- Capacity Requirements Planning
- MRP shop order launch & order maintenance (message filters and “noise management”)
- ability to aggregate disparate requirements across multiple products by work center, supplier, product
- central stores of inventory
- multi-level inventory: stores, pick, kit, move, queue
- batch processing
- demand leveling difficult and uneconomical

2 thoughts on “Replenishment Strategies”
Do you have a reference that digs into this segmentation method more?
Try
https://www.resourcesystemsconsulting.com/blog/demand-segmentation-one-size-fits-none/
Manufacturing for Survival – Blair Williams
Lean Sigma: A Practitioner’s Guide – Ian Wedgewood
http://www.tbmcg.com/misc_assets/DemandSegmentation_TBM_CarlisleTW.pdf
http://www.supplychainsegmentation.com/index